Multiple time frame analysis is a crucial technique used by traders to assess a currency pair’s market behaviour by analyzing it across various time frames. This approach provides a broader view of the market, enabling traders to identify trends, key support and resistance levels, and overall market structure that might not be visible on just one time frame. By using this method, traders can reduce the likelihood of false signals and increase their chances of making profitable trades.
Traders can choose any time frame that aligns with their personal trading strategy, whether it be weekly, daily, hourly, or 15-minute charts. However, the challenge (or opportunity) with multiple time frame analysis is that different time frames of the same currency pair may sometimes present contradictory signals. For instance, on a daily chart, EUR/USD might show a strong uptrend, while on a 4-hour chart, the pair may indicate the beginning of a downtrend. This is why it’s essential to consider the market holistically across various time frames before making a trade.
In this lesson, we’ll explore how multiple time frame analysis can be used to your advantage. By understanding how to navigate different time frames, you can enhance your decision-making and improve the precision of your trades.
Understanding Your Trading Style
Before diving into multiple time frame analysis, it’s crucial to first determine your trading style, as this will influence the time frames you’ll focus on. In a previous lesson, we discussed the different types of traders, such as scalpers, day traders, and swing traders. It’s important to revisit that section and identify which type of trader you are, as your chosen style will guide you in selecting the most appropriate time frames to analyze.
For instance, long-term traders (position traders) typically require more starting capital to withstand the market’s larger price movements and use wider stop losses to accommodate volatility over weeks or months. Short-term traders, such as scalpers or day traders, don’t need as much capital and use much smaller time frames to capture quick movements. For most retail traders, swing trading and day trading are the most popular strategies.
The Importance of Top-Down Analysis
One of the main principles behind multiple time frame analysis is the concept of top-down analysis. This is the process of starting your analysis on a larger time frame and gradually zooming into smaller time frames to refine your trade setup. By doing so, you get a better understanding of the overall market context before focusing on your chosen time frame.
To highlight the importance of top-down analysis, let’s walk through an example of what could happen when it’s neglected.
Imagine you’re analyzing a 15-minute chart for the EUR/CAD currency pair. Based on your analysis, you’ve drawn a trendline indicating an uptrend, and price appears to be bouncing off a key support level. You interpret these signals as bullish and decide to place a buy order.
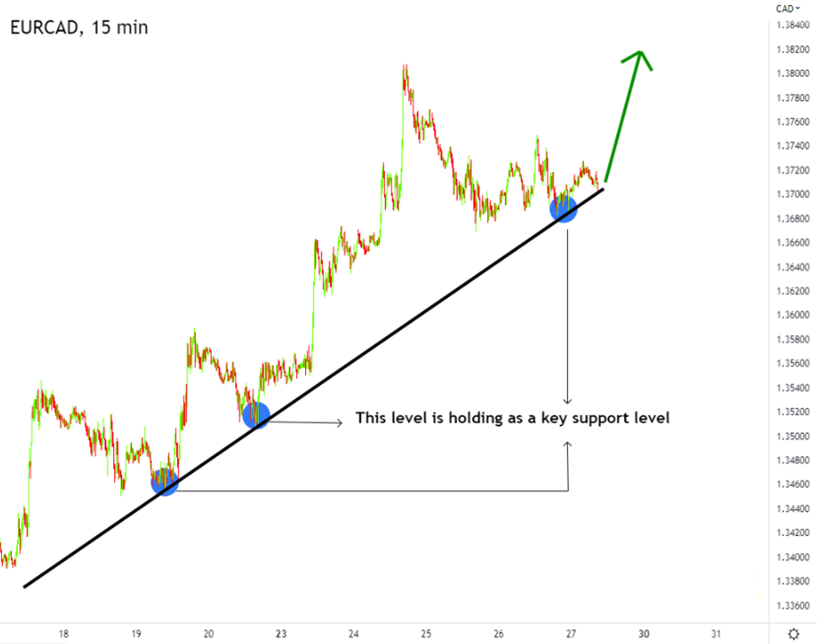
Figure: Analysis signaling a buy.
Now, let’s assume that shortly after entering the trade, price breaks below the trendline and starts to fall sharply. At this point, you’re likely experiencing frustration and confusion. “What went wrong? The setup looked perfect! Is the market out to get me?”
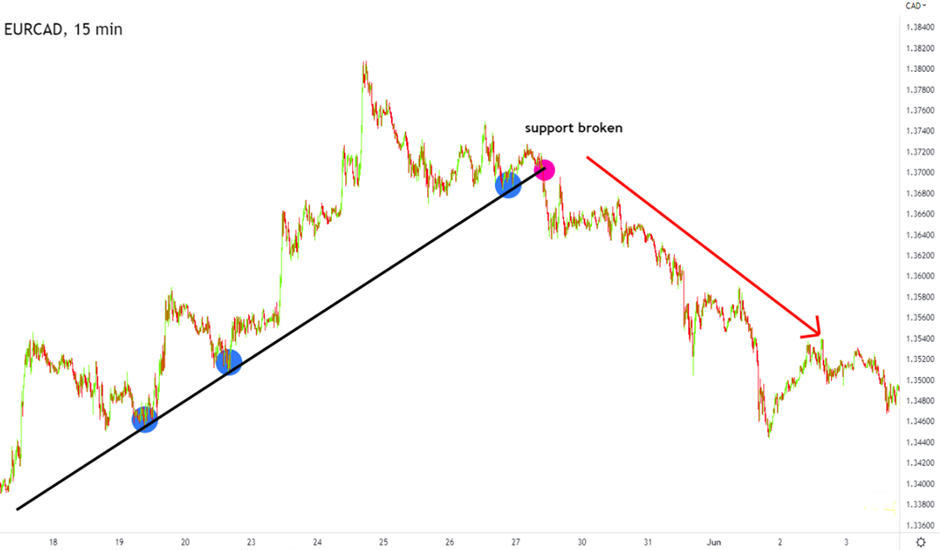
Figure: Price breaking the trendline and falling.
The issue here is that by focusing solely on the lower time frame (15-minute chart), you’ve missed the bigger picture. If you had zoomed out to analyze the 1-hour or 4-hour chart, you would have seen that price was nearing a significant resistance level. Your buy order would have been placed at the top of the market, a common pitfall for traders who fail to conduct top-down analysis.
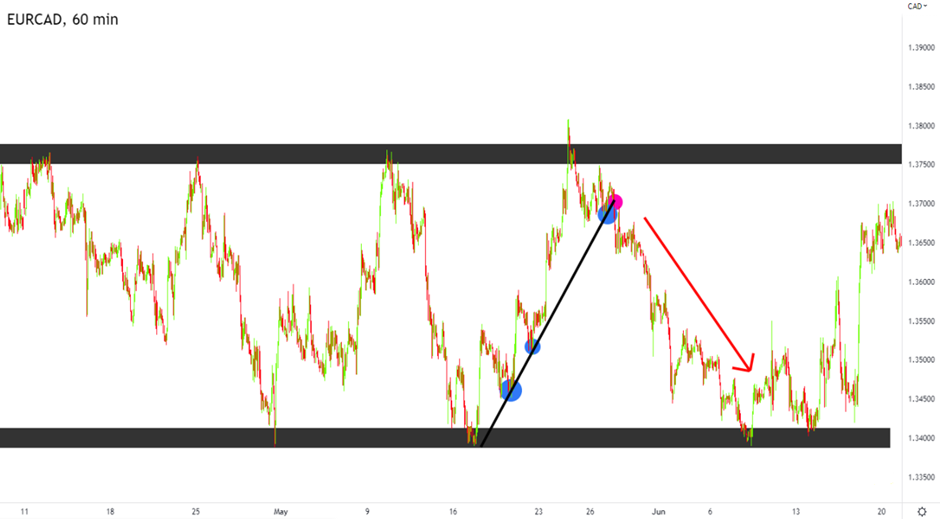
Figure: A ranging market; the trader bought near the resistance level.
This is the key lesson: failing to perform top-down analysis often results in trades being placed at suboptimal locations, such as buying at resistance or selling at support. By zooming out to higher time frames, you gain a more accurate picture of the market’s structure and sentiment.
How to Perform Top-Down Analysis
Now that we understand the importance of top-down analysis, let’s dive into how to implement it. The basic idea is to begin by analyzing larger time frames and gradually zoom in. For instance, if you plan to trade on the 1-hour chart, start your analysis on the daily or 4-hour chart first.
Let’s consider the case of a day trader. Day traders usually start by looking at the 4-hour chart to identify the overall market trend. This chart helps determine whether the market is trending, ranging, or showing signs of reversal. In this time frame, you’re primarily looking for major support and resistance levels and trend directions.
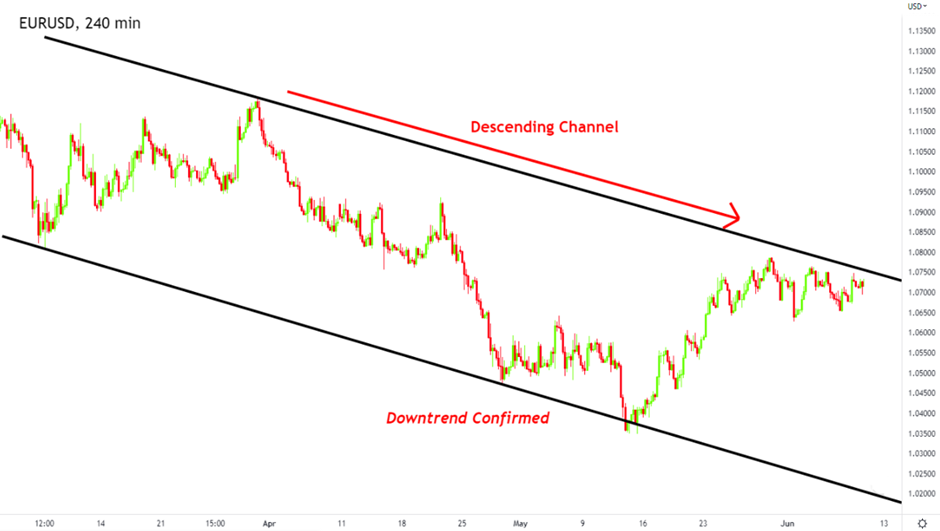
Figure: EUR/USD 4-hour chart showing a descending channel.
In our example, the 4-hour chart of EUR/USD shows that the market is moving within a descending channel. This indicates that the broader market sentiment may be bearish, although price is still in a short-term uptrend. Once you’ve identified this, you move down to the 1-hour chart, which is where most of the analysis takes place.
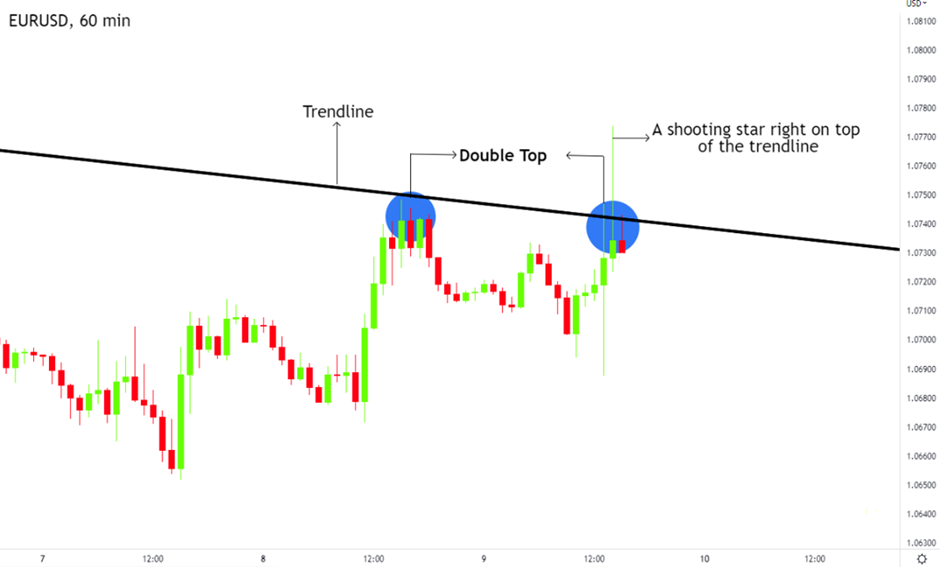
Figure: A double top and shooting star on the trendline.
On the 1-hour chart, you may spot a double top pattern forming near the upper boundary of the descending channel, accompanied by a shooting star candlestick. These patterns confirm that the market may soon reverse to the downside. The confluence of these signals gives you strong confirmation for a potential sell trade. Some traders may choose to add indicators such as moving averages or RSI for further confirmation, but the price action alone often provides sufficient information.
Once you have identified the market’s overall direction and confirmed your bias on the 1-hour chart, you can then zoom down to the 15-minute chart to pinpoint an entry point. In this lower time frame, look for price rejection, candlestick formations, or trendline breaks to refine your entry.
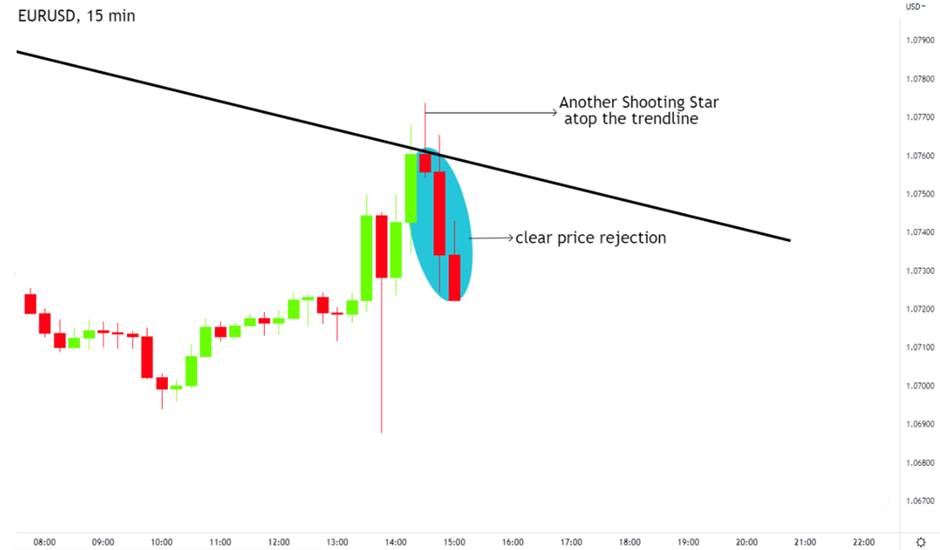
Figure: Price rejecting the trendline.
In our case, the 15-minute chart shows clear price rejection off the trendline, signalling that the downward move predicted by the higher time frames is starting. You can now enter the trade confidently, knowing that your analysis across multiple time frames aligns with the broader market sentiment.
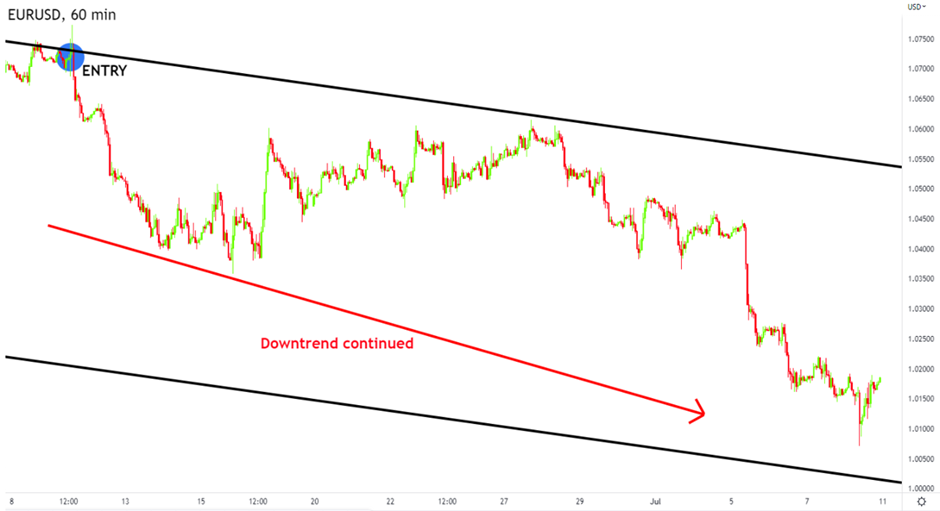
Figure: Price falling from the entry point, validating our top-down analysis.
How Many Time Frames to Use
While top-down analysis generally involves using three time frames, it’s possible to analyze more if needed. However, using fewer than three time frames is not recommended as it limits your perspective on the market.
Below is a list of popular time frame combinations:
- 1-minute, 5-minute, 30-minute
- 5-minute, 30-minute, 4-hour
- 15-minute, 1-hour, 4-hour
- 30-minute, 4-hour, daily
- 1-hour, 4-hour, daily
- 4-hour, daily, weekly
- Daily, weekly, monthly
Each combination serves different trading styles. For example, scalpers use shorter time frames, while position traders prefer longer ones.
Multiple time frame analysis is a powerful tool when used correctly, allowing traders to make more informed decisions and avoid the pitfalls of over-relying on one time frame. By incorporating this technique into your trading strategy, you can better anticipate market moves, avoid false signals, and increase your overall profitability. Always start your analysis on higher time frames and work your way down to ensure that your trades align with the broader market structure.
